Failover for REST and Web Services
Using Membrane API Gateway you can set up a high availability cluster of Services. But you can also use the gateway for a cluster of HTTP servers.
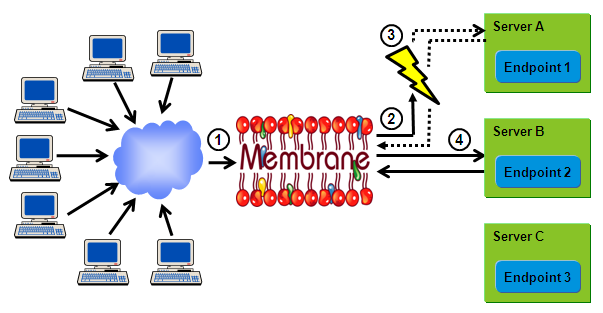
Figure1:
How it works
In figure 2 you can see how failover is realized in the Membrane Router. First the HTTPEndpointListener is receiving a request. Next the RuleMatchingInterceptor looks up a matching rule and puts that rule into the exchange data structure. Suppose the rule found is configured with a Loadbalancing interceptor. Then the Loadbalancing interceptor handles the exchange and adds a list of possible destinations. The destinations are ordered according to the dispatching strategy. Now the HTTP client component takes the first destination out of the exchange and tries to send the message to this destination. If a network error occurs, the HTTP client tries again with the next destination.
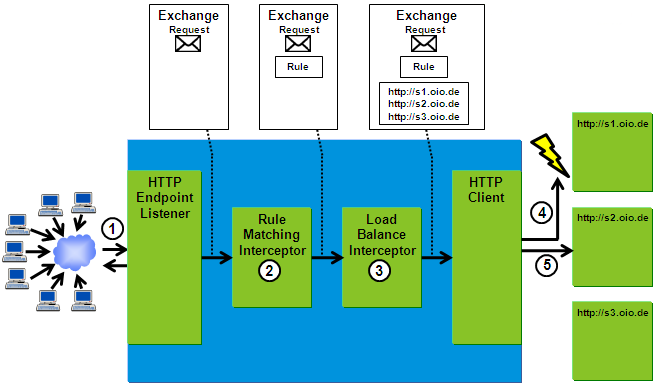
Figure2:
What failures are covered?
Network Failures
Membrane Router handles the following network failures:
- Host not reachable
The computer that is hosting the service is not reachable. - Connection refused
There is no server listening at the targetport on the target host. Maybe the server crashed. - Connection closed
The TCP connection was closed before the response from the service was received.
Besides these errors other network errors also trigger a failover.
HTTP Failures
It is hard to decide if a HTTP error was caused by a defective service or by a faulty client request. Because of that the router assumes that a HTTP error is normal server behavior and the service is working. In case you need a different behavior please let us know. We are glad to discuss the issue at the Membrane Router Mailing List.
Logging
Set the logging level to debug to see how the router handles a service failure.
Configuration
To setup a high availability cluster of Web Services just configure loadbalancing.